A project’s capacity to attract a large audience determines its success in decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), or the metaverse.
Blockchain projects must reach a larger audience and get as many user wallets as quickly as feasible. The question is, how do amateur blockchain engineers accomplish this?
There are also dozens of other cryptocurrencies on the market. Still, few offer customers actual benefits—or find their footing and ascend to the top despite direct competition from other top coins and tokens. Avalanche is one such cryptocurrency asset. Avalaunch delivers a frictionless, secure, rapid, and low-cost launchpad to catapult forthcoming initiatives to their full potential.
But what is Avalanche, and how does it work? Let’s explore what Avalanche is, how it operates, and how it leverages the AVAX coin, one of Ethereum’s most notable competitors.
What is Avalanche (AVAX)?
Avalanche is a decentralized platform designed to handle transactions more quickly, securely, and efficiently. Avalanche, one of Ethereum’s most successful rivals, was created by Ava Labs in 2020.
The intention for the creation of the blockchain platform was to make sure that it would be smart contract-capable, which means it would automatically execute contracts when specific criteria were satisfied. Avalanche’s key goals are to improve existing blockchain technology, specifically regarding scalability, interoperability, and usability.
AVAX, the native token of the Avalanche ecosystem, acts as the network’s medium of exchange and is utilized for various functions, including transaction fees and staking. Staking AVAX allows users to secure the network while also earning currency. The Avalanche consensus combines the finest features of both classical and Nakamoto consensus to build a new, leaderless blockchain that employs the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus process.
Avalanche (AVAX) is a cryptocurrency and blockchain platform competing against Ethereum. AVAX is the native coin of the Avalanche blockchain, which, like Ethereum, employs smart contracts to facilitate various blockchain applications. Let’s contrast Avalanche and Ethereum to discover what they have in common and which is preferable.
Features of Avalanche
Avalanche is an open-source platform for developing decentralized apps in a single, interoperable, and highly scalable ecosystem. The Avalanche smart contract platform supports decentralized applications (Dapps) and autonomous blockchains. Here are some of the characteristics that make Avalanche unique:
Blazingly Fast: Avalanche uses the quickest consensus process of any layer 1 blockchain. The unique consensus mechanism allows for speedy finality and low latency; in less than 2 seconds, your transaction is effectively executed and validated.
Coin creation rate: AVAX’s maximum supply is 720 million tokens. However, users can control how quickly new coins are created. AVAX holders can influence the rate of new coin creation by voting on the amount of AVAX paid as a reward for adding a new block to the Avalanche network.
Scalability: Avalanche is highly energy-efficient and can readily run on consumer-grade hardware. The entire Avalanche network uses the same amount of energy as 46 US households, equivalent to 0.0005% of the energy consumed by Bitcoin.
Transaction fee structure: Transaction processing costs vary according to the type of transaction and Avalanche’s network congestion. All fees are burned or withdrawn from circulation, so AVAX becomes scarcer over time. Avalanche users vote on the Avalanche transaction charge. Therefore, AVAX fees are subject to change.
Participation incentives: High uptime and quick reaction times can increase the number of AVAX prizes that a network participant can earn for processing transactions.
Pros and Cons of Avalanche (AVAX)
Despite Avalanche’s (AVAX) exciting features, there are many things to like and dislike about the platform. Let’s dive into the pros and cons of Avalanche (AVAX).
| PROS OF AVALANCHE | CONS OF AVALANCHE |
|---|---|
| Fast transaction processing times. | To compete with systems like Ethereum. |
| The reward structure encourages involvement. | Avalanche validators must invest 2,000 AVAX tokens. |
| Capable of hosting many blockchain-based initiatives. | There is no punishment for malicious or careless validators. |
How does Avalanche consensus work?
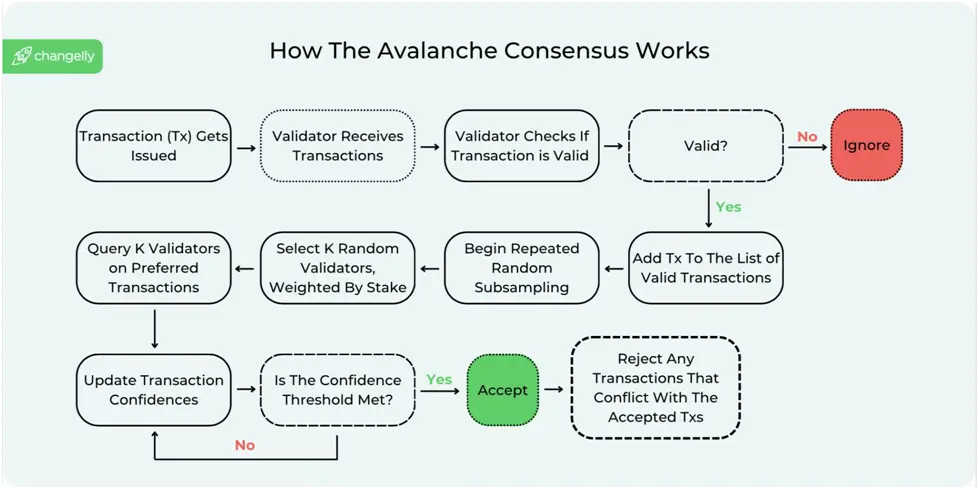
Avalanche (AVAX) is built on a novel platform that addresses the long-standing difficulties of blockchain technology, including scalability, security, and decentralization. At its foundation, Avalanche presents a revolutionary technique for consensus that allows the network to achieve exceptional throughput and near-instant finality, distinguishing it from traditional blockchain systems.
Avalanche’s unique consensus process combines classical and Nakamoto consensus theories. Unlike bitcoin’s proof-of-work (PoW) concept, which is based on a single chain of blocks, Avalanche uses a directed acyclic graph (DAG) structure for transactions over several chains in its ecosystem. This arrangement enables parallel processing, dramatically increasing network capacity and transaction speed.
Avalanche consensus works based on sub-sampled voting. Instead of requiring the entire network to validate a transaction, it randomly selects a subset of validators to make a rapid decision. This process is repeated in multiple rounds, increasing confidence in the transaction’s authenticity until it is effectively irreversible.
This approach enables Avalanche to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS), with transaction finality achieved in less than two seconds, significantly outperforming networks such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Avalanche employs a novel consensus process based on proof-of-stake (PoS). Validators must stake AVAX to confirm transactions on the network. Unlike many PoS-based consensus systems, each Avalanche validator checks a transaction independently before randomly selecting a subset of the other validators. If most validators in the sample disagree, each validator will revise its conclusion. All validators will continue to do this separately until consensus is obtained, usually in less than two seconds.
Because validators function independently and use only a tiny subset of other validators, the network has an excellent maximum transaction rate per second while simultaneously being more decentralized and scalable. The network should accelerate as it grows.
Avalanche network
Avalanche is the first ecosystem intended to handle the size of global finance while providing near-instant transaction finality. Because of how it operates at the base level, Avalanche reaches finality in less than two seconds, whereas Ethereum takes one minute.
Avalanche comprises primary networks that all use a specific subnet to host three blockchains: the exchange chain (X-chain), contract chain (C-chain), and platform chain.
C-Chain is a smart contract chain that supports the development of any Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) smart contract. The C-Chain API is compatible with Geth’s API and allows for the deployment and execution of smart contracts written in Solidity.
The C-Chain is an instance of the Coreth Virtual Machine.
The P-Chain handles all validator and subnet-level actions. P-Chain is in charge of creating and tracking new subnets and blockchains. It is also where Avalanche validation and staking take place.
The P-Chain is an instance of the platform virtual machine.
The X-Chain manages activities on digital smart assets known as Avalanche Native Tokens. X-Chain is used to carry out transactions, and its primary function is to assist with sending and receiving AVAX, Avalanche’s cryptocurrency.
AVAX is one of the assets traded on the X-Chain. When you send a transaction to a blockchain through Avalanche, you pay a charge in AVAX.
The X-Chain is an instance of the Avalanche virtual machine (AVM).
What are subnets?
Subnets let developers establish blockchains with bespoke rules, regulations, and features tailored to their needs.
Subnets are best suited for specific applications like private company blockchains, government or regulatory-compliant blockchains, gaming networks, and decentralized finance (Defi) ecosystems. They can enforce precise legal compliance, privacy settings, and performance measurements as needed for their use case.
Each subnet can have its own governance model, allowing communities to create consensus methods and regulations tailored to their blockchain. A single subnet validates each blockchain. However, a subnet can validate numerous blockchains.
Validators on a subnet help protect the Avalanche mainnet (primary network). This dual-duty system primarily provides high security for the mainnet and the multiple subnets. Subnets operate independently, although they are not isolated. They can connect with other subnets and the primary network, allowing interoperability within the Avalanche ecosystem.
How does Avalanche work?
Avalanche runs uniquely by utilizing three independent yet interconnected blockchains, each with a specific role in the network’s operation.
The X-Chain creates and manages assets. The C-Chain aims to make it easier to create smart contracts by supporting ERC-20 tokens, decentralized applications, and NFTs. Finally, the P-Chain’s job is to coordinate validators and facilitate the establishment of application-specific blockchains known as subnets.
To use Avalanche, token holders must move their tokens from one chain to another, depending on what they intend to do with them.
A comparison between Avalanche and Ethereum
The dispute over “Avalanche vs Ethereum” has been a popular subject among cryptocurrency fans and investors. Both platforms have unique features and advantages. But which is better?
Avalanche is a decentralized technology that enables highly scalable and configurable blockchain networks. Unlike standard blockchains, which function on a single, static chain, Avalanche uses a proprietary consensus system known as the Avalanche consensus. It enables the establishment of several interoperable blockchains, which improves scalability and efficiency.
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that creates a peer-to-peer network for securely executing and validating application code. Ethereum (ETH) is the second most popular cryptocurrency, following bitcoin. Vitalik Buterin and Gavin Wood founded the project in 2015.
Ethereum introduced the concept of “smart contracts”—self-executing contracts whose terms are explicitly encoded into code. This breakthrough enabled the development of decentralized apps (Dapps) on its platform.The Avalanche consensus protocol coordinates network nodes and processes transactions. It improves network security by running random checks on validators’ transaction confirmations. This strategy raises the likelihood that a transaction is genuine.
Differences between Avalanche and Ethereum
What distinguishes Avalanche from Ethereum? Avalanche and Ethereum are well-known brands in the blockchain world, each serving as a core blockchain platform with unique qualities but some essential commonalities. While both aspire to transform the way decentralized applications and smart contracts work, their approaches differ in several ways. Here are some of the main distinctions between Avalanche and Ethereum:
Consensus mechanism: Avalanche employs consensus, a unique protocol that enables fast transaction finality and high throughput. Ethereum, on the other hand, uses proof-of-stake (PoS).
Native token utility: Avalanche’s native token, AVAX, is used to pay staking and transaction fees. Ethereum’s token, ETH, has considerable utility, including being used for gas costs, staking, and collateral on several Defi systems.
Fees: Transaction fees on Ethereum, particularly during network congestion, can be expensive. Avalanche’s concentration on minimal prices results in a more predictable and economical fee structure for users and developers.
Scalability: Avalanche’s unique architecture of numerous interoperable blockchains allows it to handle thousands of transactions per second (TPS). While facing scalability issues in its current form, Ethereum is working on solutions such as sharding and layer 2 scaling to enhance TPS.
Adoption: Due to its age, Ethereum has gained greater adoption and recognition in the crypto community. Despite its youth, Avalanche is making significant progress in relationships and integration.
While both aspire to transform the way decentralized applications and smart contracts work, their approaches differ in several ways. These distinctions extend beyond technical standards, including beliefs, community engagement, and long-term ambitions. Understanding these distinctions allows consumers, developers, and investors to determine which platform best suits their needs.
Key similarities between AVAX and ETH
Decentralization: Both platforms stress decentralization, ensuring no single entity controls the network. This decentralization is critical to their security, trustworthiness, and resilience to censorship.
Smart contracts: Both Avalanche and Ethereum enable the creation and execution of smart contracts. These self-executing contracts allow for automation and trustless interactions on the blockchain.
Native tokens: Both blockchains feature native tokens (AVAX for Avalanche and ETH for Ethereum) essential for network operations, including transaction fees, staking, and network security.
Security: Security is a primary concern for both Avalanche and Ethereum. They use a variety of procedures, including consensus protocols and cryptographic techniques, to assure the security and integrity of their networks.
Open-source: Both projects are open-source, which means that developers from all over the world can contribute, audit, and build on their codebases. This openness encourages innovation and community involvement.
Avalanche and Ethereum, two blockchain titans, have unique answers to decentralization, scalability, and interoperability concerns. Both platforms are dedicated to open-source development, community interaction, and the revolutionary power of blockchain technology.

What is the AVAX token?
AVAX is the native token of the Avalanche blockchain, and it plays a vital part in the Avalanche ecosystem due to its value. It is the principal utility token for Avalaunch. AVAX allows users to invest in the Avalaunch network to boost sales. The token pays transaction fees, safeguards the blockchain through staking, and facilitates transactions between Avalanche’s numerous subnets.
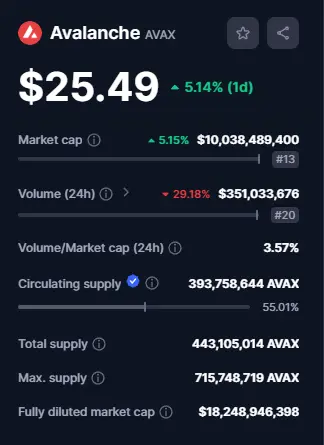
At the time of writing, the AVAX was trading at $25.60. The 24-hour trading volume is $231,842,899, representing a 0.37% market decline over the last 24 hours. The entire market capitalization of the XAVA coins is $10,868,237,392. AVAX is currently rated #11 on CoinMarketCap. (Data from CoinMarketCap).
- Name: Avalanche
- Symbol: AVAX
- Type: Utility
- Chain type: Multi-chain
- Current price: $25.5
- Maximum supply: 720,000,000 AVAX
- Circulating supply: 393,758,627 AVAX
AVAX Token Properties
These are the key takeaway properties of the design of the AVAX economic model:
- The resources spent by a validator for staking are proportional to that validator’s total stake.
- The rewards accumulated by a validator for validating are proportional to that validator’s total stake.
- Since Avalanche is leaderless, there are no “rich-get-richer” compound effects. Validators who lock their stake for longer are rewarded more.
- Validators are incentivized to stay online and operate correctly, as their rewards are based on proof-of-uptime and proof-of-correctness.
- AVAX is a capped-supply token, with a maximum cap of 720 million tokens.
- While capped, AVAX is still governable. The rate at which the maximum cap is reached is subject to governance.
- Fees are not paid to any specific validator. Instead, they are burned, thus increasing scarcity of the AVAX.
How do I buy AVAX tokens?
- Go to any exchange and create an account by entering your email ID and password.
- Set up your fund password by entering settings; this password will be asked during fund withdrawal.
- To buy AVAX tokens, you must complete KYC with the proper documents.
- After KYC, go to Spot Trade, search for AVAX, and select.
- After opening the new page, fill in the amount in AVAX or USDT you want to buy, and click the buy button.
- After a successful buy, go to the Wallet > Withdraw page.
- Here, select AVAX, and then enter the wallet address.
- It will ask you for your fund password, 2FA, and email code; enter them correctly and submit.
- Your AVAX will arrive in your wallet after a few confirmations.
Conclusion
Avalanche (AVAX) is a cryptocurrency and blockchain platform that competes with Ethereum and is notable for its speed and scalability. Various descriptions show that several blockchain networks are slow, expensive, and sophisticated. As a result, amateurs are frequently excluded from competition. Avalaunch promises a frictionless decentralized fund drive launch pad that puts novices and professional developers on the same level.